🗓️ 03022025 1132
📎
query_engine
Benefits
Distributed Execution
- An execution plan is represented by a directed acyclic graph (DAG) that consists of asynchronous operators
- Execution plans can express a variety of complex queries and fit the data storage model of Hologres
Allows Query Optimizer (QO) can easily optimize the queries based on a variety of optimization technologies
Fully asynchronous execution
HQE provides an end-to-end fully asynchronous framework
- Can eliminate the bottleneck of a high concurrency system
- Make full use of resources
- Minimizes impact of the read latency caused by the storage_disaggregation_architecture
Vectorization and column-oriented processing
HQE processes data in a vectorized manner in operators whenever possible
- HQE is deeply integrated with Storage Engine (SE)
- Flexible execution models are built to take full advantage of a variety of indexes.
- vectorization and materialization are deferred as much as possible to prevent unnecessary data reads or computing
Adaptive incremental processing
HQE implements adaptive incremental processing for regular real-time data
Optimization of specific queries
Hologres QE provides unique optimization for specific queries
Query execution process
Hologres QE contains multiple workers. The following figure shows how a worker executes a query that is initiated by a client
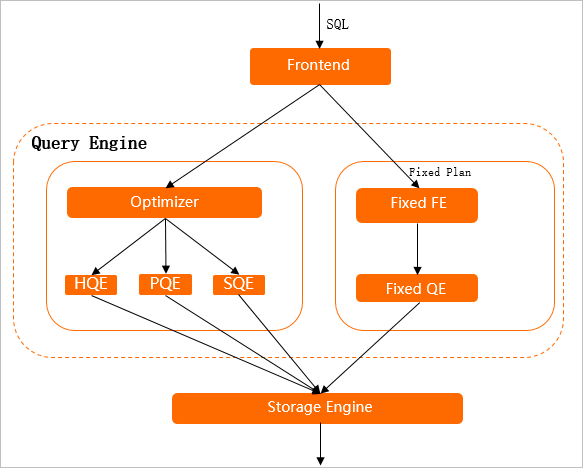
After a client initiates an SQL query, the query is executed in the following process:
- FE
- authenticates and parses the SQL query
- distributes the SQL query to different modules of HQE
- HQE
- selects an execution path based on the characteristics of the SQL query
- point query:
- the FE distributes the SQL query to Fixed QE to obtain data by skipping QO
- This shortens the execution path and improves query performance
- This execution path is called a fixed plan
- Point queries, similar to key-value queries in HBase, and point writes are processed by using fixed plans
- OLAP query:
- the FE distributes the SQL query to QO
- QO parses the SQL query and generates an execution plan
- The execution plan includes information such as the estimated cost for operator execution, statistics, and query range that is narrowed down
- QO determines to use HQE, PostgreSQL Query Engine (PQE), Seahawks Query Engine (SQE), or Hive Query Engine (Hive QE) to compute the operators based on the execution plan.
Hologres Query Engine (HQE)
main module of QE
- Uses a scalable Massively Parallel Processing (MPP) architecture to implement full parallel computing
- Uses vectorization operators to make maximum use of CPUs and achieve ultimate query performance. HQE is the
PostgreSQL Query Engine (PQE)
provides compatibility with PostgreSQL
- PQE supports a variety of PostgreSQL extensions, such as PostGIS and user-defined functions (UDFs) that are written in PL/Java, PL/SQL, or PL/Python
- The functions and operators that are not supported by HQE can be executed by using PQE
- HQE has been continuously optimized in each version
- The final goal is to integrate all features of PQE.
Seahawks Query Engine (SQE)
Allows Hologres to seamlessly connect to MaxCompute
- Provides high-performance access to all types of MaxCompute files, without the need to migrate or import data
- Also allows Hologres to access complex tables such as hash tables and range-clustered tables, and implement interactive analysis of PB-level batch data.
After Hologres QE determines the correct execution plan, Hologres QE uses SE to obtain data, merges the data from different shards, and returns the query result to the client.