🗓️ 03022025 1107
📎
hologres_segment_key
If you want to perform UPDATE operations based on primary keys or perform queries that involve range filter conditions on large-sized datasets, you can configure event time columns for tables. The system sorts data files based on the event time columns and combine the data files. This reduces duplicate files and filters out files as many as possible. This way, the query efficiency is improved. Proper settings of event time columns help improve the processing efficiency, query speed, and overall performance of databases. This topic describes how to configure event time columns for tables in Hologres.
Overview
In Hologres V0.9, the name of the segment_key property is renamed event_time_column by default. However, the segment_key property can still be used in Hologres V0.9 and earlier.
Event time columns are applicable to the following scenarios:
-
Queries that contain range filter conditions, including equivalent conditions.
-
UPDATE operations based on primary keys.
An event time column needs to be specified for a table when you create the table. The following syntax is used to configure an event time column:
-- Syntax supported in Hologres V2.1 and later
CREATE TABLE <table_name> (...) WITH (event_time_column = '[<columnName>[,...]]');
-- Syntax supported in all Hologres versions
BEGIN;
CREATE TABLE <table_name> (...);
call set_table_property('<table_name>', 'event_time_column', '[<columnName> [,...]]');
COMMIT;
The following table describes parameters in the preceding syntax.
| Parameter | Description |
| table_name | The name of the table for which you want to configure the event time column. |
| columnName | The name of the column that you want to configure as the event time column. |
Usage notes
-
We recommend that you configure the columns where data monotonically increases or decreases, such as timestamp columns, as event time columns. The event_time_column property is applicable to columns that are strongly correlated with time, such as log and traffic columns. Appropriate setting of this property can improve query performance. After multiple files are merged, if data in the event time column is unordered, the data in each file has no distinguishing features and remains unordered. In this case, the data filtering effect is poor.
-
If a table does not contain columns where data monotonically increases or decreases, you can add an
update_timecolumn and use it as the event time column. Each time you perform the UPSERT operation, the current time is written to the update_time column. -
Data queries based on event time columns follow the leftmost matching principle. Therefore, we recommend that you do not specify multiple event time columns for a table. Otherwise, data queries based on the event time columns cannot be accelerated in some scenarios. In most cases, we recommend that you specify one or two event time columns for a table.
Limits
-
The event time columns of a table must meet the NOT NULL constraint. In Hologres V1.3.20 to V1.3.27, you can specify a column that contains null values as an event time column. In Hologres V1.3.28 and later, you cannot specify a column that contains null values as an event time column. This is because if an event time column contains null values, data accuracy may be adversely affected. If you must specify a column that contains null values as an event time column based on your business requirements, you can add the following SET command before the CREATE TABLE statement:
set hg_experimental_enable_nullable_segment_key = true;You can execute SQL statements to check whether event time columns contain null values. Sample statements:
WITH t_base AS (
SELECT
*
FROM
hologres.hg_table_info
WHERE
collect_time::date = CURRENT_DATE
),
t1 AS (
SELECT
db_name,
schema_name,
table_name,
jsonb_array_elements(table_meta::jsonb -> 'columns') cols
FROM
t_base
),
t2 AS (
SELECT
db_name,
schema_name,
table_name,
cols ->> 'name' col_name
FROM
t1
WHERE
cols -> 'nullable' = 'true'::jsonb
),
t3 AS (
SELECT
db_name,
schema_name,
table_name,
regexp_replace(regexp_split_to_table(table_meta::jsonb ->> 'segment_key', ','), ':asc|:desc$', '') segment_key_col
FROM
t_base
WHERE
table_meta::jsonb -> 'segment_key' IS NOT NULL
)
SELECT
CURRENT_DATE,
t3.db_name,
t3.schema_name,
t3.table_name,
jsonb_build_object('nullable_segment_key_column', string_agg(t3.segment_key_col, ',')) as nullable_segment_key_column
FROM
t2,
t3
WHERE
t3.db_name = t2.db_name
AND t3.schema_name = t2.schema_name
AND t3.table_name = t2.table_name
AND t2.col_name = t3.segment_key_col
GROUP BY
t3.db_name,
t3.schema_name,
t3.table_name; -
You cannot modify the event_time_column property. If you want to modify the property, create another table.
-
You cannot configure the event_time_column property for a row-oriented table.
-
By default, the first non-null column of the TIMESTAMP or TIMESTAMPTZ data type in a column-oriented table is used as an event time column. If such a column does not exist, the first non-null column of the DATE data type is used as an event time column by default. In versions earlier than Hologres V0.9, no event time column is specified for a table by default.
-
The columns of the DECIMAL, NUMERIC, FLOAT, DOUBLE, ARRAY, JSON, JSONB, BIT, and MONEY data types and other complex data types are not supported.
How it works
The following figure shows how data in a shard is written.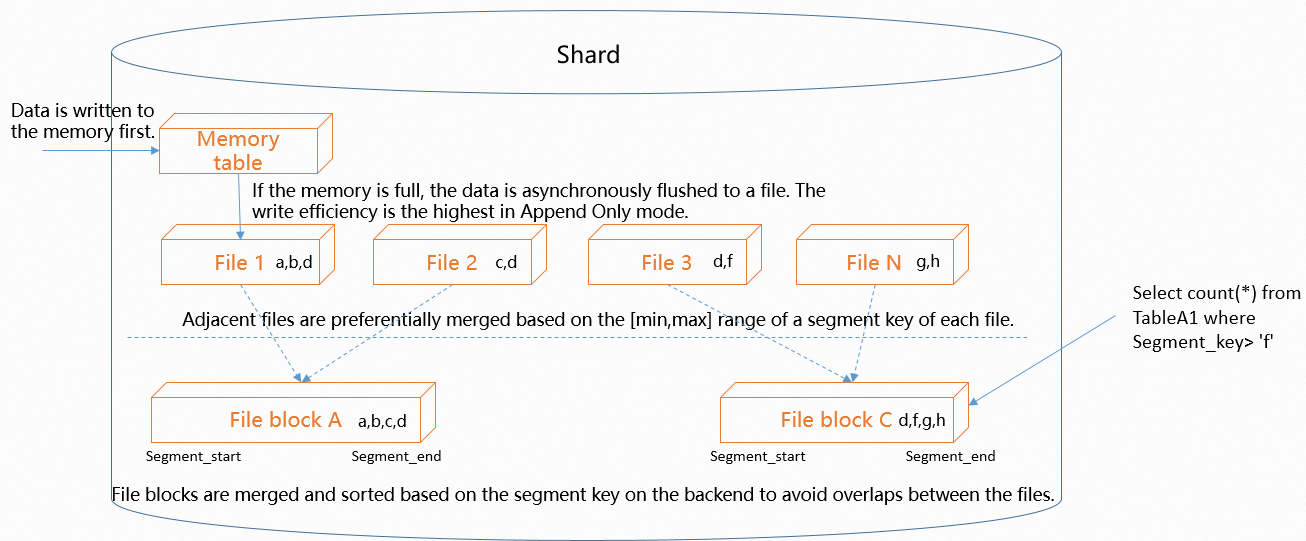
-
Data in a shard is written to a memory table first. To achieve the maximum write efficiency, the append-only mode is used to write data. The size of the memory table is limited. When the memory table is full, Hologres asynchronously flushes the data in the memory table to files.
-
To maximize write efficiency, data is written to files in append-only mode, and the number of files increases over time. In this case, Hologres periodically merges the files. If the event_time_column property is configured, Hologres sorts the files based on the range specified by the property, selects the files whose data has adjacent ranges, and then merges these files. This reduces the overlap between the files and filters out unnecessary files during queries. In this case, query efficiency is improved.
-
Files are sorted based on event time columns. Data queries based on event time columns follow the leftmost matching principle. If you specify columns
a,b, andcas event time columns, the query of columnsa, b, and cor columnsa and bcan hit the event time columns. If you query columnsa and c, only the query of columnacan hit the event time columns. If you query columnsb and c, the query cannot hit the event time columns.
The preceding content indicates that event time columns can be used to accelerate data queries in the following scenarios:
-
Queries that contain range filter conditions, including equivalent conditions.
If the column that you want to query is specified as an event time column, when Hologres scans data, Hologres compares the statistics (min/max) of the columns in files based on the range filter conditions to filter the required files. This accelerates the query process.
-
UPDATE operations based on primary keys.
In Hologres, the
UPDATEoperation is equivalent to the combination of theDELETEoperation and theINSERToperation. After you configure a primary key for a table, if you execute the UPDATE statement or the INSERT ON CONFLICT statement, Hologres finds the values of the event time column that you specify for the destination table based on the primary key. Then, Hologres finds the file where the existing data resides based on the event time column. Finally, Hologres locates the existing data and marks the data as DELETE. For more information about the UPDATE statement and the INSERT ON CONFLICT statement, see UPDATE or INSERT ON CONFLICT(UPSERT). An appropriate event time column helps quickly locate the file where the existing data resides. This improves write performance. A large number of files need to be scanned during a data query in the following scenarios: (1) No event time column is specified for the column-oriented table. (2) The event time column that you configure is not appropriate. (3) The event time column that you configure is not strongly correlated with time and contains unordered data. In this case, a large number of I/O operations are performed, and the CPU load is high. As a result, the write performance and the loads of the instance are negatively affected.
Examples
-
Configure a column as the event time column when you create a table.
-
Syntax supported in Hologres V2.1 and later:
CREATE TABLE tbl_segment_test (
a int NOT NULL,
b timestamptz NOT NULL
)
WITH (
event_time_column = 'b'
);
INSERT INTO tbl_segment_test values
(1,'2022-09-05 10:23:54+08'),
(2,'2022-09-05 10:24:54+08'),
(3,'2022-09-05 10:25:54+08'),
(4,'2022-09-05 10:26:54+08');
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM tbl_segment_test WHERE b > '2022-09-05 10:24:54+08'; -
Syntax supported in all Hologres versions:
BEGIN;
CREATE TABLE tbl_segment_test (
a int NOT NULL,
b timestamptz NOT NULL
);
CALL set_table_property('tbl_segment_test', 'event_time_column', 'b');
COMMIT;
INSERT INTO tbl_segment_test VALUES
(1,'2022-09-05 10:23:54+08'),
(2,'2022-09-05 10:24:54+08'),
(3,'2022-09-05 10:25:54+08'),
(4,'2022-09-05 10:26:54+08');
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM tbl_segment_test WHERE b > '2022-09-05 10:24:54+08';
You can query the execution plan by executing the EXPLAIN statement. If the execution plan contains
Segment Filter, the query hits the event time column.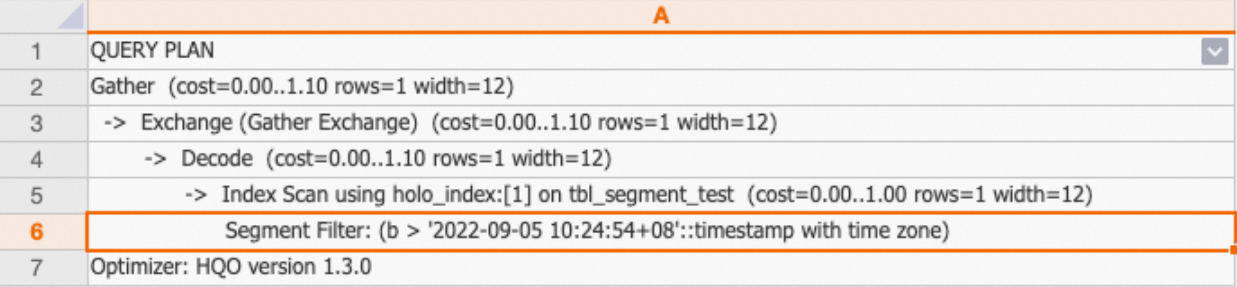
-
-
Configure multiple columns as event time columns when you create a table.
-
Syntax supported in Hologres V2.1 and later:
CREATE TABLE tbl_segment_test_2 (
a int NOT NULL,
b timestamptz NOT NULL
)
WITH (
event_time_column = 'a,b'
);
INSERT INTO tbl_segment_test_2 VALUES
(1,'2022-09-05 10:23:54+08'),
(2,'2022-09-05 10:24:54+08'),
(3,'2022-09-05 10:25:54+08'),
(4,'2022-09-05 10:26:54+08')
;
-- The query cannot hit the event time columns.
SELECT * FROM tbl_segment_test_2 WHERE b > '2022-09-05 10:24:54+08';
-- The query hits the event time columns.
SELECT * FROM tbl_segment_test_2 WHERE a = 3 and b > '2022-09-05 10:24:54+08';
SELECT * FROM tbl_segment_test_2 WHERE a > 3 and b < '2022-09-05 10:26:54+08';
SELECT * FROM tbl_segment_test_2 WHERE a > 3 and b > '2022-09-05 10:24:54+08'; -
Syntax supported in all Hologres versions:
BEGIN;
CREATE TABLE tbl_segment_test_2 (
a int NOT NULL,
b timestamptz NOT NULL
);
CALL set_table_property('tbl_segment_test_2', 'event_time_column', 'a,b');
COMMIT;
INSERT INTO tbl_segment_test_2 VALUES
(1,'2022-09-05 10:23:54+08'),
(2,'2022-09-05 10:24:54+08'),
(3,'2022-09-05 10:25:54+08'),
(4,'2022-09-05 10:26:54+08')
;
-- The query cannot hit the event time columns.
SELECT * FROM tbl_segment_test_2 WHERE b > '2022-09-05 10:24:54+08';
-- The query hits the event time columns.
SELECT * FROM tbl_segment_test_2 WHERE a = 3 and b > '2022-09-05 10:24:54+08';
SELECT * FROM tbl_segment_test_2 WHERE a > 3 and b < '2022-09-05 10:26:54+08';
SELECT * FROM tbl_segment_test_2 WHERE a > 3 and b > '2022-09-05 10:24:54+08';
-
References
-
For more information about how to configure table properties based on business query scenarios, see Guide on scenario-specific table creation and tuning.
-
For more information about the DDL statements for Hologres internal tables, see the following topics: